The core difference between single-beam LED bulbs and traditional halogen lamps
In the field of automotive lighting, the difference between single-beam LED bulbs and traditional halogen lamps is as obvious as day and night. These differences are fundamentally different from optical structure design to energy efficiency life parameters, and then to regulatory compliance, which profoundly affects the choice and usage experience of car owners.
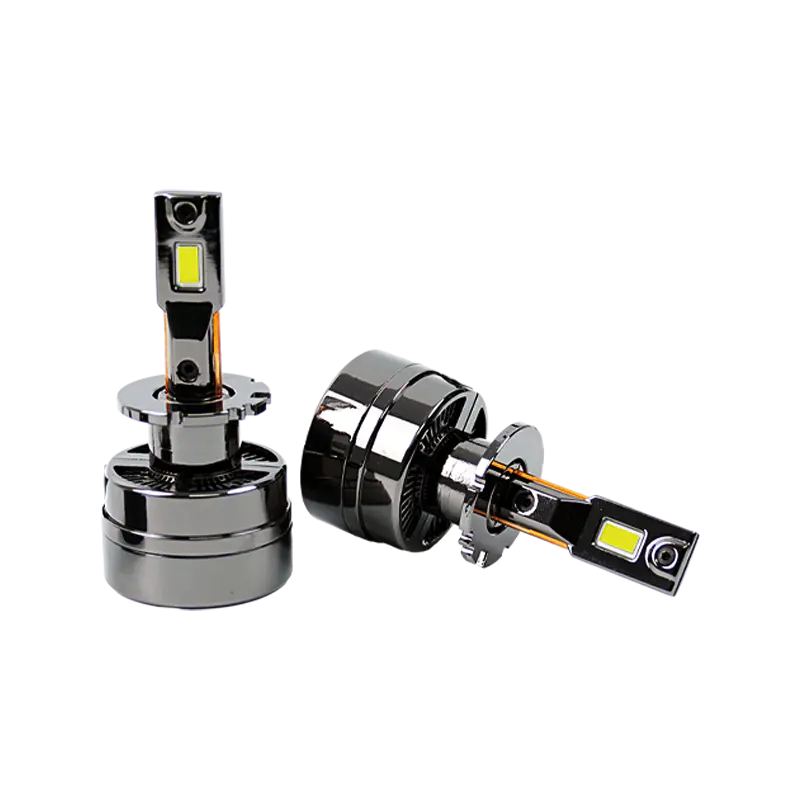
In terms of optical structure design, traditional halogen lamps use the principle of tungsten filament light emission, and generate light by heating the tungsten filament to an incandescent state with electric current. The light is divergent and has no clear directionality, and requires a complex combination of reflectors and lenses to focus the light to form the required lighting beam. Single-beam LED bulbs use semiconductor chips to emit light, with a small and concentrated light-emitting area. Through the precise optical lens design, the light can be accurately controlled in a specific direction, reducing light scattering and improving lighting efficiency and uniformity. For example, when the light of traditional halogen lamps illuminates the road surface, a large amount of light will be wasted in invalid areas, while LED bulbs can focus the light on the road surface that needs to be illuminated, effectively improving the night driving vision.
In terms of energy efficiency and life parameters, the performance gap between the two is significant. When halogen lamps are working, a large amount of electrical energy is converted into heat energy, and only a small part of the electrical energy is converted into light energy. The luminous efficiency is extremely low. Generally, the luminous flux of a 55W halogen lamp is only about 1000 lumens. In contrast, the luminous efficiency of a single-beam LED bulb can reach 3-5 times that of a halogen lamp. The luminous flux of a 55W LED bulb can easily exceed 3000 lumens. In terms of life, the tungsten filament of a halogen lamp will gradually sublimate and become thinner at high temperatures, and eventually fuse, with an average life of only 500-1000 hours. LED bulbs do not have a filament structure, and their semiconductor chips have a theoretical life of 30,000-50,000 hours under normal working conditions, which can almost accompany the entire use cycle of the vehicle, greatly reducing the replacement frequency and maintenance costs.
Regulatory compliance is also an important aspect that distinguishes the two. Different countries and regions have different regulatory requirements for automotive lighting fixtures. After a long period of development, the relevant regulatory standards for traditional halogen lamps have become very mature and complete, with strict regulations on light type, brightness, color temperature, etc. As an emerging lighting product, single-beam LED bulbs have many advantages, but they still face challenges in regulatory adaptability. Some regions require LED bulbs to pass specific certification tests to ensure that their light type meets road lighting specifications and does not cause glare interference to other vehicles and pedestrians. At the same time, there are corresponding requirements for the electromagnetic compatibility of LED bulbs to avoid interference with other electronic equipment in the vehicle when they are working.
Three technical indicators for choosing single beam LED replacement bulbs
When car owners decide to replace single-beam LED replacement bulbs for their cars, the three major technical indicators of lumen value and color temperature matching principle, substrate heat dissipation design evaluation and original vehicle circuit compatibility detection are the key to ensuring that suitable bulbs are purchased.
The principle of matching lumen value and color temperature is the primary consideration. Lumen value represents the luminous intensity of the bulb. The higher the value, the brighter the light. However, the higher the lumen value, the better. Too high a lumen value may cause the light to be too strong, causing glare to oncoming vehicles and pedestrians, affecting traffic safety. Generally speaking, the lumen value of the low beam is more suitable between 2000 and 3000 lumens, and the high beam can be appropriately increased to 3000-4000 lumens. Color temperature affects the color of the light. Common color temperatures range from 3000K (warm yellow light) to 6500K (cold white light). Warm yellow light with a lower color temperature has stronger penetration in rainy and foggy weather, while cold white light with a higher color temperature has a clearer visual effect, but it is easy to scatter in rainy and foggy weather, reducing visibility. Therefore, car owners should choose the appropriate color temperature according to the climatic conditions of the area and personal usage habits. For example, in areas where people often drive in rainy and foggy weather, a color temperature of about 4300K is more suitable.
The evaluation of substrate heat dissipation design is directly related to the service life and performance stability of LED bulbs. LED bulbs will generate a certain amount of heat when working. If the heat cannot be dissipated in time, the chip temperature will rise, which will reduce the luminous efficiency, shorten the service life, and even cause damage to the bulb. High-quality LED bulbs usually use large-area aluminum substrates or copper substrates as heat dissipation materials. These materials have good thermal conductivity and can quickly transfer heat. At the same time, with the design of efficient cooling fans or cooling fins, the heat dissipation effect is further enhanced. When purchasing, car owners can observe the heat dissipation structure of the bulb, check whether the cooling fins are dense and whether the fan is running smoothly. If necessary, they can consult the merchant to understand the heat dissipation materials and heat dissipation methods.
The compatibility test of the original vehicle circuit is also an important link that cannot be ignored. The circuit systems of different models are different. The working current and starting method of LED bulbs are different from those of traditional halogen lamps. If the newly replaced LED bulbs are incompatible with the original vehicle circuit, problems such as flickering and fault alarms may occur. Before purchasing, car owners should understand the circuit parameters of their vehicles, check the vehicle user manual or consult professional maintenance personnel. Some LED bulbs are equipped with intelligent decoding functions that can automatically adapt to the circuit systems of different models, but they still need to be tested after installation to ensure that the bulbs work properly and will not cause damage to the vehicle circuit.

 English
English Español
Español عربى
عربى русский
русский